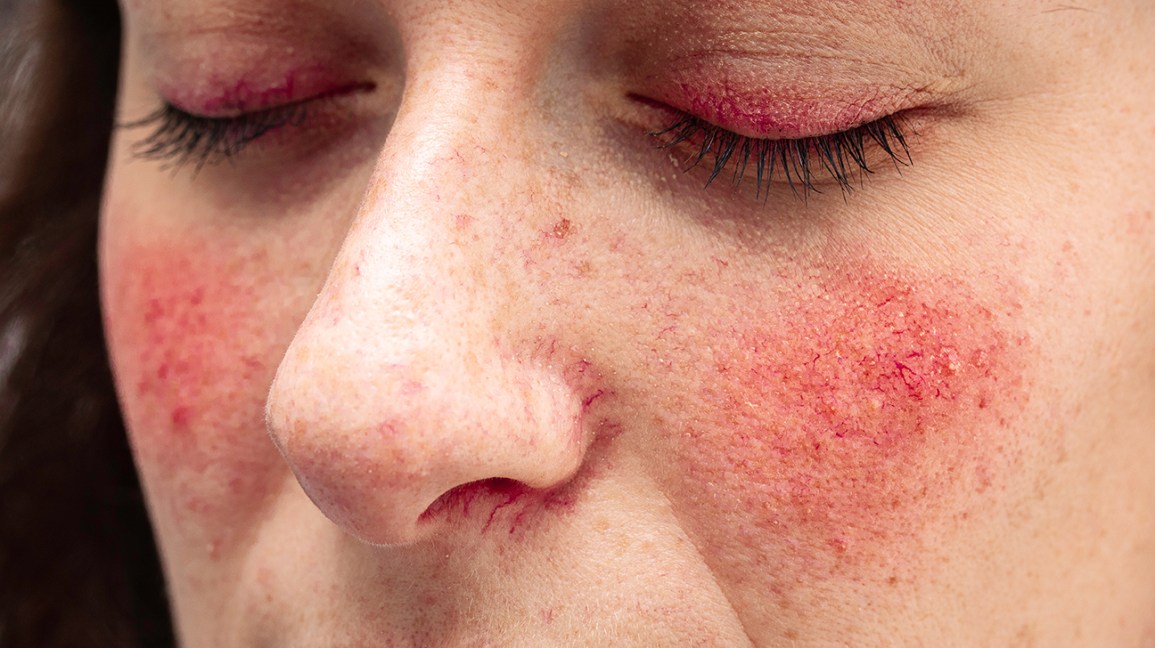
Rosacea, which usually affects the face, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. Rosacea may be mistaken by people for acne, eczema, or an allergic skin reaction.
Facial flushing, irritated skin, and pimples are the main symptoms of rosacea. Other signs include quick blushing and trouble with the eye.
Rosacea, which affects about 1-20 percent of the population, is normal. However, when they have rosacea, people always obtain the incorrect diagnosis, so the true incidence could be much higher.
There is currently no cure for rosacea, but with creams and medications, people can treat the symptoms.
Some foods and drinks, such as dairy products, spicy foods, caffeine and alcohol, can exacerbate the symptoms. Sun exposure can exacerbate the symptoms as well.
In females, rosacea is more common than in males and typically occurs after the age of 30.
An overview of rosacea, including its therapies, causes, symptoms, home remedies, and potential complications, is given in this article.
Pictures
Treatments
While there is no cure at present, the symptoms of rosacea can be relieved by different treatments.
The symptoms can get worse over time without treatment.
The best outcomes are usually achieved from a combination of drugs and lifestyle changes. Some potential treatment options for rosacea are looked at in the following sections.
Skin creams
Inflammation and skin discoloration may be minimized by skin creams. Once or twice a day, doctors may suggest using them. Topical antibiotics, tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid are examples.
Camouflage creams that mask blemishes on the skin may also be recommended by a doctor.
Eye drops
Eye drops, which occur in ocular rosacea, may alleviate eye symptoms.
For example, a kind of steroid eye drop called blephamide might be recommended by a doctor. They can recommend this, followed by a break or a tapered use, for a few days to a week.
Antibiotics
Anti-inflammatory effects can occur with oral antibiotics. They tend to give results that are faster than topical ones. Tetracyclin, minocycline, and erythromycin are examples.
Tetracyclines are antibiotics that can be effective for symptoms of the eye. Doxycycline in people with ocular rosacea helps relieve dryness, scratching, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light.
Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin (Accutane) is an oral drug used by individuals in serious cases of rosacea (if other treatments have not worked). This is a strong medicine that protects the skin from releasing oil. The side effects can be severe.
For individuals with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, this drug is not helpful.
Laser treatment
Laser therapy may be used by dermatologists to help decrease visible blood vessels, or telangiectasia. To shrink them, this procedure utilizes intense pulsed light.
Although some discomfort can be caused by the procedure, most individuals will not need an anesthetic. Laser therapy can cause bruising, skin crusting, swelling, tenderness, and very rarely, infection at times.
They should talk to a cosmetic surgeon if a person wants to remove thickened skin that has formed due to rosacea.
Excess skin may be removed by laser therapy or scalpel surgery. A carbon dioxide laser can also shrink thickened tissue.
Types
According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), there are four primary types of rosacea:
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea: Symptoms include skin discoloration, flushing, and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular rosacea: Symptoms include flushing, swelling, and breakouts that resemble acne.
- Phymatous rosacea: Symptoms include thickened, bumpy skin.
- Ocular rosacea: Symptoms include eye redness and irritation and swollen eyelids.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of rosacea can differ greatly from individual to individual.
In individuals with lighter skin, rosacea is more common. In these skin tones, however the signs of rosacea are easier to recognize and few studies have investigated the occurrence of rosacea in people with darker skin.
In most cases of rosacea, the following symptoms tend to be present:
- Persistent skin discoloration: This may look like a blush or sunburn that does not go away. It happens when hundreds of tiny blood vessels near the surface of the skin expand.
- Skin thickening: The skin may get thicker from excess skin tissue. This usually affects the nose and can cause rhinophyma, which affects males much more than females.
- Flushing: This occurs when the face temporarily darkens. It may spread from the face down to the neck and chest, and the skin may feel unpleasantly hot.
- Skin bumps and pimples: Small, red, acne-like bumps may develop. These may contain pus.
- Visible blood vessels: Also called spider veins, or telangiectasia, this commonly affects the cheeks, bridge of the nose, and other parts of the central face.
- Eye irritation: People may have irritated, watery, or bloodshot eyes. The eyelids can become red and swollen (blepharitis), and styes are common. Rosacea affects the eyes in around 50% of people with the condition. Rarely, vision can become blurred.
People may also have the following secondary symptoms of rosacea:
- burning or stinging sensations in the skin
- facial swelling, due to excess fluid and proteins leaking out of the blood vessels
- dry or rough facial skin
The following symptoms may be useful indicators of rosacea in darker skin:
- a warm feeling most of the time
- dry, swollen skin
- patches of darker skin, or a dusky brown discoloration to the skin
- persistent acne-like breakouts
- hard, yellowish-brown bumps around the mouth, eyes, or both
- a burning or stinging sensation when applying skin care products
- swollen or thicker skin on the forehead, nose, cheeks, or chin
Causes
Experts don’t know what’s triggering rosacea. Many think, however that the following variables can contribute:
- Abnormalities in the blood vessels: Skin specialists suggest that facial flushing and spider veins are due to abnormalities in the blood vessels of the face. However, they are unsure as to what causes inflammation in the blood vessels.
- A skin mite called Demodex folliculorum: This mite lives on the skin and usually causes no problems. However, people with rosacea tend to have more of these mites than others. It is unclear whether the mites cause the rosacea or the rosacea causes the increase in mites.
- Bacteria called Helicobacter pylori: These gut bacteria stimulate the production of bradykinin, a small polypeptide that causes blood vessels to dilate. Experts suggest that this bacterium may play a role in the development of rosacea.
- Family history: Many people with rosacea have a close relative with the condition. This means that there may be an inherited or genetic component.
Triggers
For many individuals, dietary factors can affect the symptoms of rosacea. Symptoms can be caused or worsened by consuming the following foods and drinks:
- hot foods and beverages
- caffeine
- dairy products
- spices and seasonings that contain capsaicin, such as hot sauce, cayenne pepper, and red pepper
- alcohol, including wines and hard liquors
- foods containing cinnamaldehyde, such as tomatoes, chocolate, and citrus fruits
It can decrease the risk of flare-ups and help manage rosacea by avoiding one or more of these foods and beverages.
Some variables can worsen rosacea by raising blood flow to the surface of the skin. These include:
- extremes of temperature
- sunlight, humidity, and wind
- stress, anxiety, anger, and embarrassment
- vigorous exercise
- hot baths and saunas
- some medications, such as corticosteroids and drugs for treating high blood pressure
- acute medical conditions, such as a cold, cough, or fever
- some chronic medical conditions, such as hypertension
Natural remedies
Minimizing exposure to the causes of rosacea can help avoid its symptoms. Adopting good practices for skin care can also improve.
If a person uses them alongside medical treatments, the following lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage symptoms:
- Avoid rubbing or touching the face.
- Wash the face with a gentle cleanser, and avoid using products that contain irritants or alcohol.
- Avoid comedogenic products. These block the oil and sweat gland openings.
- Keep the skin hydrated with a gentle moisturizer. Wait for topical medications to dry before moisturizing.
- Wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen when outdoors.
- In cold weather, protect the face with a scarf or ski mask.
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
- Avoid foods and beverages that might trigger an outbreak.
- Avoid using over-the-counter steroid creams unless a doctor has recommended them. These may worsen symptoms in the mid to long term.
- Use an electric shaver when shaving, as this is less likely to trigger flare-ups than a normal razor.
Some individuals find that pre-foundation creams and powders use green or yellow to help mask the discoloration of the skin.
Reducing stress
A common cause for rosacea is stress. Taking any action to decrease levels of stress can help reduce flare-ups.
For certain people, rosacea may be a source of stress. It can make someone feel embarrassed, frustrated, anxious, or low in self-confidence.
It may help people to regulate their emotions by being well informed about rosacea, as they can feel more in control and better equipped to manage any potential complications or recurrences.
It can also help to pursue appropriate care and if necessary, talk to a psychiatrist or mental health professional.
Diagnosis
For rosacea, there is no clinical test. After examining the skin of the person and asking about their symptoms and causes, a doctor may make a diagnosis. It will allow the doctor to differentiate it from other skin disorders by the existence of enlarged blood vessels.
A distinct or coexisting diagnosis is generally indicated by the presence of a rash on the scalp or ears. The signs and symptoms of rosacea occur predominantly in the face.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment will reduce the risk of progression dramatically. The doctor may order blood tests or refer the individual to a dermatologist if the doctor suspects that there may be an underlying medical condition, such as lupus.
Summary
Rosacea is an acute inflammation skin condition. Symptoms include facial flushing, eye symptoms, and skin thickening.
Although there is no cure at present, people will take medicines to relieve the symptoms. Also, home remedies can help.
An individual can talk to a doctor about any concerns about rosacea.